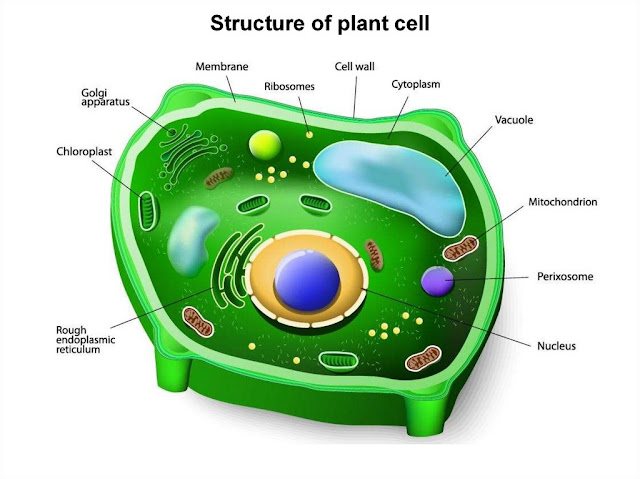
The cell is the fundamental unit of life. Every living organism existing on the planet earth are composed of a cell. The cell differs in their size, shape and the number.
A Plant cell contains different types of specialized organs which are involved in various biological functions in plants including photosynthesis, transportation, transpiration, excretion, and lot more. All these functions occur in different parts of plants. The complete process of photosynthesis occurs in the leaf of a plant and is divided into different sub-layers. Chloroplasts play a primary role in photosynthesis. Before learning about the Chloroplasts, let us learn what are Plastids?
Plastids are the main sites of photosynthesis in all autotrophs. The term Plastids is derived from the Greek word plastikas meaning moulded. They are oval shaped, double membrane-bounded organelle, present in the plant cell of all green plants, photosynthetic bacteria, algae, and other eukaryotic organisms. Andreas Franz Wilhelm Schimper, a German botanist, was the first person to discover and coin the term Plastids in the year 1885.
Plastids are the site of production and storage of important biochemical compounds, which are later used by the plant cells. This organelle usually comprises of pigments used in photosynthesis, and the types of pigments in a plastid determine the cell’s colour. According to the plant cell diagram, these plastids are present within the meristem cells of the plant cell.
Based on the pigments, the plastids are classified into:
1. Chloroplasts– They are green coloured plastids which are present in the leaves and play a significant role during photosynthesis
2. Chromoplasts– They are bright and dark coloured plastids, typically found in the flowers, and fleshy fruits.
3. Leucoplasts– They are colourless or white colour plastids, which are commonly found in all growing tissues and in other colourless flowers.
Role of Plastids in Plant Cell:
1. Helps in the storage of protein, starch and oil
2. Deliver various colours to flowers and fruits
3. Plastids provide essential metabolic and signalling functions
4. Traps solar energy to synthesise food through the process of photosynthesis
5. Maintains the balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere
These were some information related to plastids and their role in the plant cell.
For more information on plant cell and its organelles, students can visit BYJU’s website and also learn by watching interactive video lessons on various topics by subscribing to the BYJU’S YouTube Channel.